Disease Prevention Articles
In the News Osteoporosis Warning Signs
Osteoporosis is one of the most common ailments of adults over the age of 50 and it is a problem that people do not want to live with. Weak bones lead to fractures and many other scary problems that could leave you disabled.
Before turning into full-blown osteoporosis, osteopenia – the process of thinning bones - precedes the ailment. There are some warning signs to look for to determine if your bones are in fact thinning.
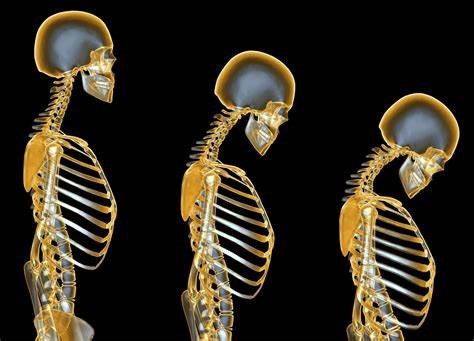
Here are nine warning signs for osteoporosis:
Warning Sign #1 - You have had more than one fracture in the past two years or a fracture that seemed severe considering the circumstances.
Warning Sign #2 – You are naturally a small or thin person.
Warning Sign #3 – You have an autoimmune condition that causes you to take prednisone or another corticosteroid.
Warning Sign #4 – You are a smoker and have been throughout your adult life.
Warning Sign #5 – You drink more than two alcoholic beverages a day.
Warning Sign #6 – You do not drink milk, or you have a lactose intolerance that prevents you from drinking milk.
Warning Sign #7 – You have an eating disorder.
Warning Sign #8 – You are an Asian or Caucasian female over the age of 50.
Warning Sign #9 – You have a family member who had osteoporosis before the age of 50 or before menopause.
Cold and Flu 101: Ways to Feel Better Soon
We are well into the cold and flu season and unfortunately everyone knows someone that has been down and out with cold and flu symptoms this year. Or even worse, COVID.
Fortunately, there are some simple ways to help you stay healthy throughout the winter.

Here are five simple ways to stay cold and flu-free:
- Load up on garlic. It contains allicin, which has antiviral properties.
- Sweat it out in the sauna. Sweating helps to release toxins in the body.
- Get the proper amount of sleep. Sleeping helps you to be more energized and helps your immune system fight off germs.
- Eat your chicken noodle soup. It contains anti-inflammatory deliciousness that strengthens disease-fighting cells.
- Have your yogurt. The probiotics help strengthen your immune system by increasing the number of white blood cells in your body.
In the News: Lyme Disease Awareness Month – Part II
(Continued from Part I…)

Another reason why Lyme Disease is hard to pinpoint in patients, is that the symptoms often vary from person to person.
Symptoms of early Lyme disease may present as “a flu-like illness (fever, chills, sweats, muscle aches, fatigue, nausea, and joint pain). Some patients have a rash or Bell’s palsy (facial drooping). However, although a rash shaped like a bull’s-eye is considered characteristic of Lyme disease, many people develop a different kind of Lyme rash or none.”
Most doctors treat Lyme Disease with a course of antibiotics. The amount and type of antibiotic is determined by length of time since the tick bite and/or suggested time since infection.
For people whose central nervous system has been affected by Lyme Disease, intravenous antibiotics and other inpatient treatment is recommended.
For people diagnosed with Lyme Disease, doctors also recommend a diet that will help avoid flare-ups due to the disease.
Gluten-free, low-sugar, low-carbohydrates, and foods that are rich in vitamins are all a suggested diet for those with Lyme Disease. Foods to avoid include dairy and refined sugars.
So how can you avoid being bit by a tick and potentially contracting Lyme Disease?
Ticks tend to be near the ground, in leaf litter, grasses, bushes and fallen logs. High risk activities include playing in leaves, gathering firewood, and leaning against tree trunks. When you hike, stay on cleared trails instead of walking across grassy fields.
Wear shoes, socks, long pants, and long sleeves. Tie back long hair and wear a hat. Light-colored clothing helps you spot ticks before they cause trouble.
In the News: Lyme Disease Awareness Month – Part I
May is National Lyme Disease Awareness Month, a chance for Lyme patients, activists, and educators to spread information on how to prevent Lyme and tick-borne diseases.

According to LymeDisease.org, “Lyme disease is a bacterial infection primarily transmitted by Ixodes ticks, also known as deer ticks or blacklegged ticks. These tiny arachnids are typically found in wooded and grassy areas. Although people may think of Lyme as an East Coast disease, it is found throughout the United States, as well as in more than sixty other countries.”
The Center for Disease Control (CDC) estimates that more than 476,000 people are diagnosed with Lyme Disease in the U.S. every year. Many experts believe the number is higher though, as people with Lyme Disease are often misdiagnosed.
Although anyone can get Lyme Disease, young children, the elderly and those with jobs that require you spend time outdoors are more prone to getting Lyme Disease.
Lyme Disease is often called “The Great Imitator,” because its “symptoms mimic many other diseases. It can affect any organ of the body, including the brain and nervous system, muscles and joints, and the heart.”
Patients with Lyme Disease are typically misdiagnosed with fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, and psychiatric illness, including depression.
Most people get Lyme Disease from the bite of a nymphal, or the immature form of the tick. Nymphs are about the size of a poppy seed and because they are so tiny, their bite is painless so many people don’t even realize that they have been bitten.
Once a tick is attached, if left undisturbed it can feed for several days. The longer it is attached, the more likely it will transmit Lyme Disease and other harmful pathogens.
(Continued in Part II…)

